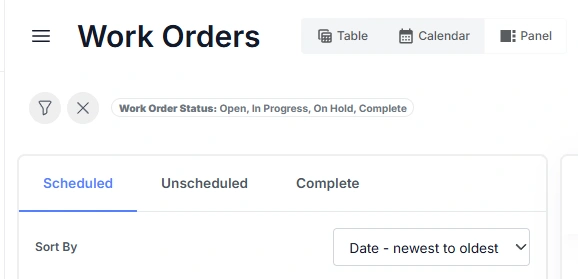
Scheduling Work Orders
In the panel view, Work Orders are grouped into Scheduled, Unscheduled, and Complete categories. This layout helps users quickly see which jobs are planned, awaiting scheduling, or finished.
| Category | Description |
|---|---|
| Scheduled | Work Orders that have been planned for execution. For Standard Assets, this means a schedule date has been assigned. For Advanced Assets, it means the Work Order has been added to an Event, which defines when the asset will be offline for maintenance. |
| Unscheduled | Work Orders that are not yet planned. For Standard Assets, these have no schedule date set. For Advanced Assets, these have not been linked to an Event. Unscheduled Work Orders represent outstanding maintenance tasks that still need to be assigned a time or event. |
| Complete | Work Orders that have been finished and marked with the status Complete. These records provide a historical view of work that has already been performed. |
How Scheduling Works in Samurai CMMS
In Samurai CMMS, scheduling defines when maintenance work will occur and, for Advanced Assets, when the asset will be taken offline. The scheduling process varies slightly depending on the type of asset:
By scheduling Work Orders, either through setting a schedule date (Standard Assets) or assigning them to an Event (Advanced Assets), you ensure maintenance activities are well organised, downtime is properly tracked, and resources are used efficiently. Scheduling work involves assigning dates to work orders and confirming that the right people, parts and equipment will be available when the work starts. Effective scheduling helps the team plan ahead, manage downtime and ensure work is carried out safely and on time.
Work orders can be scheduled in two ways depending on the type of asset. Advanced assets are scheduled by adding the work order to an event. Standard and basic assets use a simple scheduled date. Both methods are accessed through the Panel view.
Standard Assets
Standard Assets are scheduled by assigning a Schedule Date directly to the Work Order. This date indicates when the maintenance work is planned to begin. The Work Order’s start and end times are recorded to track the duration of the work, but downtime is not tracked separately.
Advanced Assets
Advanced Assets use Events to manage scheduling. An Event represents a defined maintenance window when the asset is unavailable for operation. Multiple Work Orders can be linked to the same Event if they are performed during that downtime. Events also allow users to record Delay Codes, providing visibility into downtime reasons and duration.
Accessing the Scheduling Tools
In the Panel view, select an unscheduled work order. Open the options menu and choose Schedule. This opens the Schedule Work Order form.
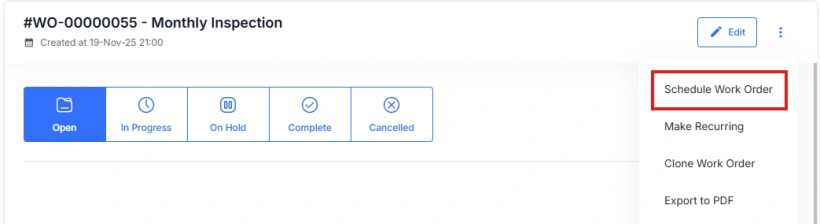
Scheduling for Advanced Assets
Advanced assets use events to organise work. Events act as containers for one or more work orders and help maintenance and operations plan downtime in a structured way.
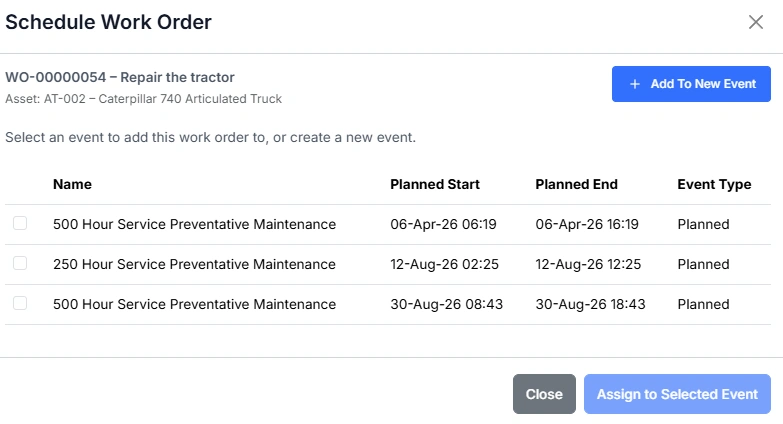
In the Schedule Work Order form you can:
Select an existing event
A list of current events for the asset is shown. Each event displays the planned start and end times and the event type. Tick the event you want to assign the work order to.
Create a new event
If no suitable event exists, select Add To New Event. This creates a new event, allowing the work order to be grouped with future tasks and managed together during the planned downtime.
This approach ensures related work is completed in the same window and helps reduce repeated downtime for the same asset.
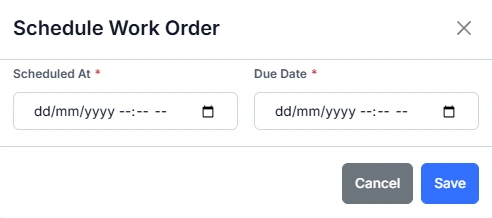
Scheduling for Standard and Basic Assets
Standard and basic assets do not use events. Instead, the work order is scheduled by setting a scheduled date.
Open the Schedule Work Order form and enter the scheduled start date. Once saved, the work order moves from Unscheduled to Scheduled.
Summary
Samurai supports efficient planning by:
- Scheduling advanced asset work through events
- Scheduling standard and basic asset work through a set date
- Providing simple scheduling tools through the Panel view
This process helps teams plan resources, coordinate downtime and complete work when it is needed.
